In order to estimate to understand environmental behaviors of radionuclides and toxic metal ions, we need to construct and extrapolate reaction models, which can describe changes of their speciation, from the results of detailed reaction studies and molecular-scale structural information. Such mechanistic models could help us to improve reliability of safety assessment of nuclear disposal and to develop efficient decontamination strategies. In our group, we are pursuing model development of sorption/binding interactions of metal ions and mineral surfaces or metal ions and natural organic matters. Possible effects of the interaction between mineral surfaces and natural organic matters on metal uptake are also of our great interests.
Identifying adsorption structures by X-ray absorption spectroscopy and density function theory simulation
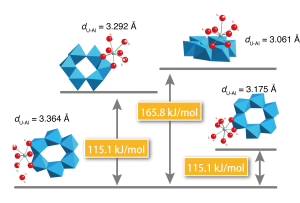
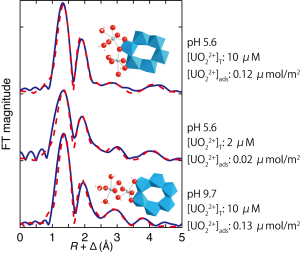
X-ray absorption spectroscopy, especially extended X-ray absorption fine structure (EXAFS) analysis, is a power analytical tool, which can be applicable for structural determination around a central metal ion in amorphous samples and sorption or solution samples that lack long-range orders. The applicability of EXAFS can be further imporved, if it is combined with molecular-scale simulations such as density functional theory calculation. In this research we’ve identified possible adsorption structures of hexavalent uranium (uranyl, UO22+) on gibbsite (α-Al(OH)3) surface, which is a representative Al-containing mineral and a model for edge sites of alumino-silicate clay minerals.
- Hattori, T.*, Saito, T., Ishida, K., Scheinost, A. C., Tsuneda, T., Nagasaki, S., Tanaka, S., “The Structure of Monomeric and Dimeric Uranyl Adsorption Complexes on Gibbsite: A Combined DFT and EXAFS Study”, Geochim. Cosmochim. Acta 73, 5975-5988 (2009).
 Development of electrostatic interaction models between humic substances and ions
Development of electrostatic interaction models between humic substances and ions
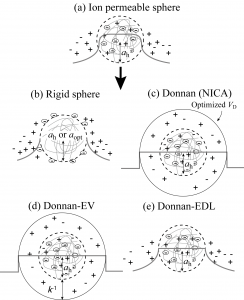
Humic substances are a collection of heterogeneous organic macromolecules resulting from decomposition and condensation of animal and plant residues. They possess many reactive functional groups on their carbon backbones and can bind various metal ions. Although there are good mechanistic interaction models, which can describe ion binding to humic substances, treatments of electrostatic interaction between cationic metal ions and negatively charged metal ions are relatively premature. In this research we’ve been studying the electrostatic interaction between ions and humic substances by direct determination of the electrostatic potential by fluorescent probes and application of sophisticated electrostatic models.
- Saito, T.*, Koopal, L. K., Nagasaki, S., Tanaka, S., “Electrostatic Potentials of Humic Acid: Fluorescence Quenching Measurements and Comparison with Model Calculations”, Colloids Surf. A 347, 27-32 (2009).
- Saito, T.*, Nagasaki, S., Tanaka, S., Koopal, L. K., “Electrostatic Interaction Models for Ion Binding to Humic Substances“, Colloids Surf. A 265, 104-113 (2005).
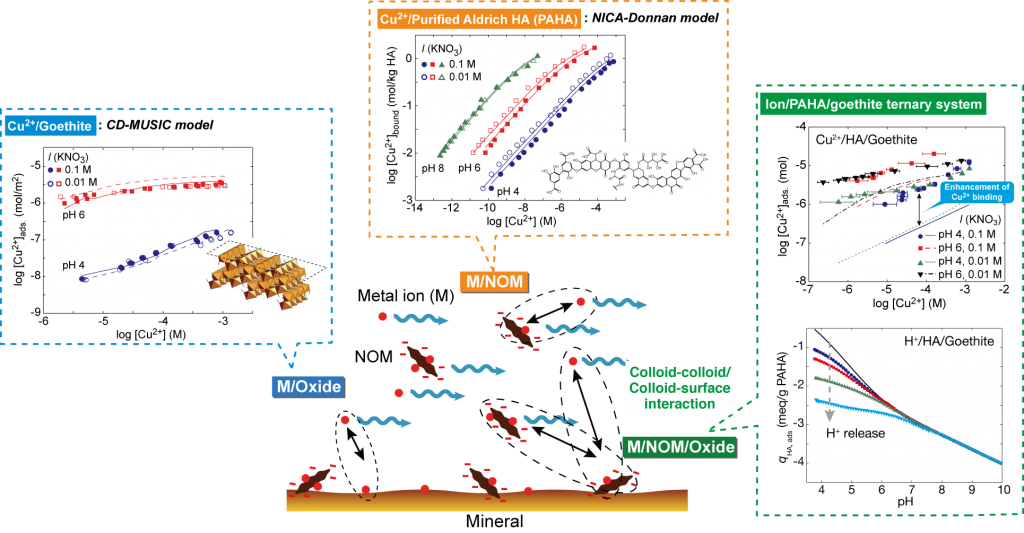
実環境は,異なる環境構成成分が共存する複雑な系であり,金属イオンの動態は,個々の成分との反応に加えて,複数の成分が関与する反応によっても影響を受ける.例えば,天然で見られる鉱物表面のほとんどは天然有機物で覆われており,そこでは,鉱物表面と天然有機物間の相互作用がイオンの分配に影響を与えることになる.本研究では,幅広い環境条件下で,腐植物質とゲーサイト(α-FeOOH)の相互作用が金属イオンの吸着に与える影響を評価し,反応の機構論的なモデル化を進めています.
- Saito, T.*, Koopal, L. K., Nagasaki, S., Tanaka, S., “Adsorption of Heterogeneously Charged Nanoparticles on a Variably Charged Surface by the Extended Surface Complexation Approach: Charge Regulation, Chemical Heterogeneity and Surface Complexation”, J. Phys. Chem. B 112, 1339-1349 (2008).
- Saito, T.*, Nagasaki, S., Tanaka, S., Koopal, L. K.:, “Analysis of Copper Binding in the Ternary System Cu2+/Humic Acid/Goethite at Neutral to Acidic pH”, Environ. Sci. Technol. 39, 4886-4893 (2005).
- Saito, T.*, Koopal, L. K., van Riemsdijk, W. H., Nagasaki, S., Tanaka, S., “Adsorption of humic acid on goethite: Isotherms, charge adjustments, and potential profiles” , Langmuir 20, 689-700 (2004).